Best Functional Medicine Tests for Healthy Adults in Their 40s
A Pathway to Aging Gracefully
Whenever I mention “functional medicine” people seem confused…
Introduction
As we reach our 40s, staying healthy and aging well becomes a priority. Functional medicine helps by addressing the root causes of aging and disease, keeping you healthier for longer. In this newsletter, I’ll cover some key tests to consider in your 40s to maintain your health as you age.
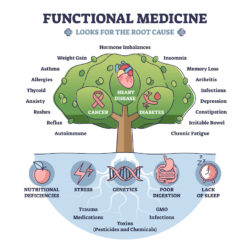
What is Functional Medicine?
Functional medicine focuses on finding and treating the root causes of disease, not just symptoms. It looks at your unique genetics, environment, and lifestyle to create a personalized health plan. Unlike traditional medicine, which usually steps in after you’re sick, functional medicine aims to prevent issues before they start. It looks at the changes in our bodies (nutritional deficits, inflammation, oxidation, mitochondrial dysfunction) and provide us with the opportunity to correct them before they become manifest as a disease.
How Functional Medicine Helps With Aging
Aging involves changes in inflammation, hormones, and cell function. These processes can be influenced by lifestyle and targeted care. Functional medicine identifies early problems in these areas, helping to slow or even reverse some aging effects.
By maintaining balance in your body, functional medicine can extend not just your lifespan but also your healthspan—the number of years you stay healthy and active.
There is no doubt that functional medicine is an addition to mainstream medicine and combined implementation ensures better outcomes.
I will give below a list of tests (mainstream and functional) that I find useful for my patients in their 40s.
Please read and do not hesitate to contact me, should you be interested in “health planning”.
Health Concerns for Adults in Their 40s
As we age, certain physiological changes begin to take place, which can affect overall health and vitality. While many of these changes are subtle, they can lead to more significant issues if left unchecked. Key concerns for adults in their 40s include:
- Hormonal changes: Men experience a gradual decline in testosterone, while women may start entering perimenopause, leading to shifts in estrogen and progesterone.
- Metabolism: Slower metabolism can make it harder to maintain a healthy weight and energy levels.
- Bone density: Both men and women are at risk for reduced bone density, increasing the risk of osteoporosis.
- Cardiovascular health: Cholesterol and blood pressure levels often rise in the 40s, increasing the risk of heart disease.
- Cognitive function: Memory, focus, and mental clarity may begin to decline due to inflammation, hormonal shifts, or oxidative stress.
Addressing these concerns early with the right tests and interventions can greatly improve health outcomes.
Top Tests for Healthy Aging
-
Comprehensive Hormone Panel
Hormone balance plays a vital role in the aging process. A comprehensive hormone panel evaluates key hormones, including:
- Men: Testosterone, DHEA, and cortisol to assess how aging affects energy, muscle mass, and stress response.
- Women: Estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, and cortisol levels to evaluate hormonal changes during perimenopause.
Balanced hormones are essential for maintaining energy, mood, and overall well-being. Identifying imbalances early can prevent weight gain, sleep disturbances, and low libido, supporting graceful aging.
-
Thyroid Function Test
Thyroid health is crucial for metabolism, energy levels, and mental clarity. The thyroid function test assesses:
- TSH, Free T3, Free T4: To evaluate thyroid activity.
- Thyroid antibodies: To detect autoimmune conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, which can cause fatigue, weight gain, and brain fog.
A well-functioning thyroid supports a healthy metabolism and prevents age-related issues like weight gain and low energy.
-
Nutritional Deficiency Testing
As we age, nutrient absorption can decline, leading to deficiencies that accelerate aging. Key nutrients tested include:
- Vitamin D: Essential for bone health, immune function, and mood.
- Vitamin B12: Supports energy and cognitive function.
- Magnesium, Iron, Zinc: Important for muscle function, metabolism, and immune health.
Addressing deficiencies early can prevent fatigue, muscle weakness, and cognitive decline, making it easier to stay healthy and active.
-
Comprehensive Stool Analysis
Gut health plays a significant role in overall well-being and aging. A comprehensive stool analysis evaluates the health of the gut microbiome, digestion, and inflammation levels. This test examines:
- Gut flora balance: Identifies beneficial bacteria versus harmful bacteria, yeasts, or parasites.
- Digestive markers: Assesses how well your body breaks down and absorbs nutrients.
- Inflammation markers: Detects gut inflammation, which can contribute to conditions like leaky gut, autoimmune diseases, and cognitive decline.
A healthy gut is linked to better immune function, hormone balance, and even mood regulation, making it essential for aging gracefully.
-
Cardiometabolic Panel
As cardiovascular health becomes more of a concern with age, a cardiometabolic panel helps assess risk factors for heart disease, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. Key markers include:
- Cholesterol and triglycerides: High levels increase the risk of heart disease.
- Glucose and insulin: Indicators of blood sugar control, with elevated levels pointing to insulin resistance or prediabetes.
- HbA1c: Provides a long-term picture of blood sugar levels, helping identify early signs of diabetes.
Addressing cardiometabolic health early can prevent conditions like heart disease, stroke, and diabetes, supporting a longer, healthier life.
-
Bone Density Test
Bone health is another critical factor in aging. A bone density test measures bone mineral density (BMD) to assess the risk of osteoporosis or fractures. While both men and women experience bone loss as they age, women face a higher risk due to menopause-related estrogen declines.
- Osteopenia and osteoporosis risk: Early detection allows for interventions such as weight-bearing exercises, dietary adjustments, or supplementation to strengthen bones.
- Calcium and Vitamin D levels: These nutrients are essential for bone health and may be part of the assessment.
Maintaining strong bones is key to preventing injuries and maintaining mobility as you age.
-
Inflammatory Marker Testing (e.g., CRP, ESR)
Chronic inflammation is a silent contributor to many age-related diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and cognitive decline. Inflammation also accelerates the aging process itself. Testing for inflammation markers such as:
- C-reactive protein (CRP): A key marker of systemic inflammation, elevated levels suggest an increased risk for heart disease and other inflammatory conditions.
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR): Measures how quickly red blood cells settle, with faster rates indicating inflammation.
Reducing inflammation through diet, lifestyle changes, and targeted supplements can improve overall health and slow down aging.
-
Genetic Testing for Personalized Health
Genetic testing provides insight into how your genes influence aging, metabolism, detoxification, and disease risk. By examining key genetic markers, functional medicine practitioners can personalize your health plan. This test can reveal:
- Detoxification pathways: Genetic variants in liver enzymes (e.g., CYP450) that affect how well your body detoxifies harmful substances.
- Hormone metabolism: Variants that influence how your body processes hormones, affecting risks for conditions like breast cancer or hormone imbalances.
- Nutrient processing: Genetic predispositions that affect your absorption or utilization of vitamins like B12, folate, and Vitamin D.
Understanding your genetic profile allows for highly personalized recommendations to optimize aging and prevent disease.
-
Detoxification Pathway Assessment
The ability to detoxify environmental toxins efficiently is essential for healthy aging. Over time, toxin exposure from pollution, pesticides, and household chemicals can lead to cellular damage and accelerate aging. A detoxification pathway assessment measures how well your body clears toxins, assessing:
- Liver function: Enzyme activity involved in breaking down and removing toxins.
- Glutathione levels: Your body’s master antioxidant, critical for detoxification and reducing oxidative stress.
Improving detox pathways through lifestyle changes, specific foods, and supplements can help protect against age-related damage and support longevity.
-
Cognitive Function Tests
Maintaining cognitive health is crucial for aging well. Functional medicine testing can assess brain function and detect early signs of cognitive decline, offering the opportunity for intervention before issues become severe. Key tests may include:
- Memory and processing speed assessments: Evaluating short-term memory, attention, and information processing.
- Mental clarity and focus: Tests to assess cognitive sharpness, which can be affected by factors like inflammation, poor circulation, and hormonal imbalances.
Addressing cognitive function early with nutrition, brain training, and lifestyle changes can help maintain mental agility and prevent age-related decline.
11. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Capacity Testing
Oxidative stress plays a significant role in the aging process and the development of age-related diseases. Functional medicine offers tests that assess the body’s balance between free radical production and antioxidant defenses. Key tests include:
- 8-OHdG (8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine): A marker for oxidative DNA damage, indicating how much oxidative stress your cells are under.
- Glutathione levels: Measuring this critical antioxidant reveals the body’s ability to neutralize oxidative damage and protect against aging.
- Lipid peroxides: These markers show the extent of damage to cell membranes due to oxidative stress, which can accelerate aging.
Addressing oxidative stress through lifestyle changes, supplementation, and dietary antioxidants can slow down cellular aging and improve overall vitality.
12. Mitochondrial Function Test
Mitochondria are the powerhouse of our cells, responsible for producing the energy (ATP) needed for every function in the body. As we age, mitochondrial dysfunction becomes more common, contributing to fatigue, cognitive decline, and metabolic issues. Functional medicine evaluates mitochondrial health through:
- ATP production levels: Assessing how efficiently your cells generate energy.
- Organic acid testing: This test reveals metabolites linked to mitochondrial activity, offering insight into how well your mitochondria are functioning.
- Oxidative phosphorylation efficiency: Identifies impairments in the energy production pathways of the mitochondria.
Improving mitochondrial function through targeted supplements (e.g., CoQ10, NAD+, PQQ) and lifestyle interventions (e.g., exercise, cold therapy) can increase energy levels and promote healthy aging.
13. Organic Acids Test (OAT)
The Organic Acids Test (OAT) provides a comprehensive look at metabolic function by evaluating by-products of metabolism that offer insight into various processes, including:
- Energy production: Measures how efficiently your body breaks down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats for energy.
- Neurotransmitter function: Assesses metabolites of dopamine, serotonin, and other neurotransmitters, providing insight into brain health and mood regulation.
- Detoxification and antioxidant status: Reveals deficiencies in antioxidants like glutathione and CoQ10, key for neutralizing toxins and oxidative stress.
- Mitochondrial markers: Shows how well your mitochondria are producing energy and managing cellular health.
The OAT test is highly valuable for identifying energy deficits and oxidative stress that contribute to aging and disease.
14. Nutrient and Metabolic Panel
Unlike standard nutrient testing, functional medicine’s nutrient and metabolic panels look deeply at how well the body is using vitamins and minerals at a cellular level. This includes:
- B-vitamin markers: Evaluates active forms of B12, folate, and other B-vitamins critical for energy production and DNA repair.
- Amino acid levels: Assesses the availability of amino acids needed for muscle repair, neurotransmitter production, and detoxification.
- Fatty acid profile: Analyzes essential fatty acids that support brain health, inflammation regulation, and hormone production.
Ensuring optimal nutrient levels supports mitochondrial function, energy metabolism, and healthy aging.